Saving for college is a goal for many parents – and with good reason. Higher education can open doors to new opportunities and set a foundation for a successful future. But understanding how to navigate college savings plans can be complex. This article will explore the different options available for obtaining funding for higher education.
You will learn the basics of college savings plans, the different types available, and the advantages and disadvantages of each. You’ll also discover the potential tax benefits associated with many college savings plans, as well as some important tips for selecting the right college savings plan for your needs. With this information, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to save for college education.
Types of College Savings Plans
When it comes to saving for college, there are several different types of college savings plans that you could choose from. Each plan has different advantages and drawbacks, and understanding the differences between them is the key to finding the right college savings plan for your child’s future.
The most popular types of college savings plans are the following:
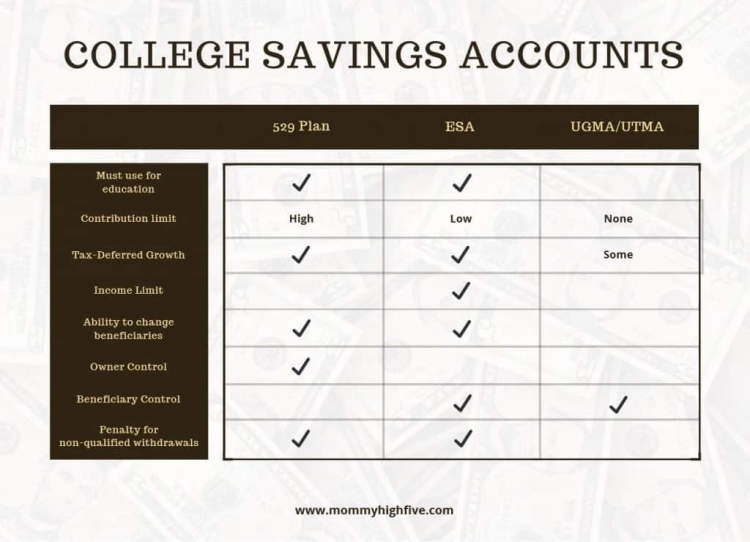
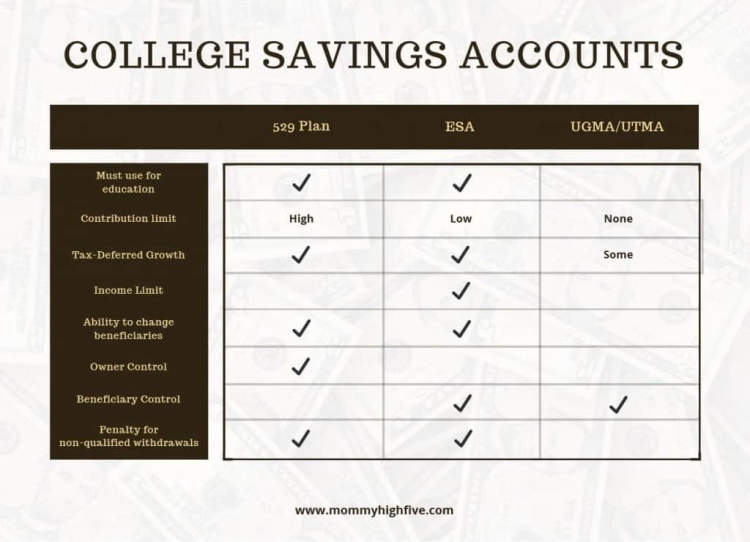
- 529 Savings Plan – A 529 savings plan is a type of tax-advantaged savings account that allows individuals to save for higher-education expenses such as tuition, fees, room and board, and even certain other expenses like books.
- Coverdell Education Savings Account – A Coverdell ESA is an individual investment account that provides a tax-free way to save money for education expenses.
- UGMA / UTMA Accounts – UGMA/UTMA accounts are custodial accounts that allow someone to contribute to a minor’s education expenses.
- Roth IRA – A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account (IRA) that allows you to set aside after-tax income to save for retirement. It can also be used as a college savings vehicle, and the money you contribute is allowed to grow tax-free.
- Prepaid College Tuition Programs – Prepaid College Tuition Plans allow you to prepay a certain amount of tuition in advance so that you are not affected by tuition increases over time.
No matter which type of college savings plan you choose, it’s important to research and understand the options available and to make sure that your savings plan fits your family’s financial goals.
Comparing Fees and Investing Options
When it comes to planning for college, it is important to make sure that you have done your due diligence and chosen the right college savings account for you. In addition to researching the different types of college savings accounts, such as 529 Plan, Education Savings Account (ESA), Coverdell ESA and UGMAs/UTMAs, it is essential to compare the fees and investing options for each one.
Before selecting a college savings account, it is important to understand the types of fees you will pay and what services and investments you have access to as an account holder. Most accounts have maintenance fees, which can vary from institution to institution. There may also be additional fees associated with particular products and services.
In terms of investment options, some college savings accounts may offer a larger selection of investments than others. Depending on the account, you may have access to stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and even ETFs. Some accounts have a predetermined set of investments, and other accounts allow you to choose from a wide range of investments. It is important to compare the fees and investing options before deciding on a college savings plan.
Below is a list of important questions to consider when comparing fees and investing options for a college savings plan:
- What is the fee structure for the account?
- What kinds of investments are available?
- Do investment selections and fees differ based on the amount invested?
- Are there any additional charges associated with transactions?
By doing your research and understanding the fees and investments costs associated with different college savings plans, you can be sure to make an informed decision that best suits your goals and needs.
Tax Implications of College Savings Plans
A college savings plan is a great tool to help you or your child pay for a college education. These plans offer certain tax benefits that can save you money when set up and managed correctly. Here’s an overview of what you need to know about the tax implications of a college savings plan.
Tax Advantages of College Savings
The biggest tax advantage of a college savings plan is that your contributions are exempt from federal income taxes. This means your contributions to the plan are largely tax-free. Furthermore, your withdrawals from the plan are also exempt from federal income taxes as long as they are used to pay qualifying expenses. Qualifying expenses typically include tuition, fees, books, and other materials used for school.
State Tax Benefits
Many states also provide tax benefits to college savings plans. Depending on the plan and state, these benefits could include tax credits, deductions, or special tax savings. Additionally, some states exclude the plan’s earnings from state income tax. It’s best to research the specific plan and state you’re considering for the best tax advantages.
Gift Tax Implications
If you’re considering contributing to a college savings plan, there are certain gift tax implications you should consider. You can contribute up to $15,000 per year to a college savings plan without incurring any gift tax. Anything over $15,000 is considered a gift and may be subject to gift pay, depending on the beneficiary’s status. It’s important to keep in mind that if you’re married or in a civil union, you and your partner can contribute up to $30,000 together without incurring any gift tax.
Overall Statutory Limitations
When contributing to a college savings plan, there are also a few limitations you should keep in mind. These include the following:
- Annual contributions are limited to $15,000 per beneficiary, per year.
- Total overall contributions are limited to $310,000 per beneficiary.
- Any gifts to a beneficiary over $15,000 may be subject to gift tax.
Conclusion
The tax implications of college savings plans can be complicated, but understanding them is an important part of making sure your finances are in order and that you’re taking full advantage of the tax benefits associated with this type of plan. Taking the time to research the specifics of the plan and your state’s particular benefits can ultimately save you money and help you reach your college financing goals.
Conclusion
Navigating college savings plans can be an overwhelming experience, but it is important to be informed in order to make the best possible choices for higher education funding. Developing a plan that works for you requires considering various factors like your financial goals, risk tolerance, and timeline. It is essential to research the different options available to ensure they meet your needs.
In the end, the best option is one that is tailored to your financial needs today and provides you with a suitable amount of flexibility for the future. With careful consideration and a well-thought-out savings plan, you can be well on your way to achieving your goals of higher education funding.